11. 蓝牙
蓝牙是一种短距通信系统,其关键特性包括鲁棒性、低功耗、低成本等。蓝牙系统分为两种不同的技术:经典蓝牙 (Classic Bluetooth) 和蓝牙低功耗 (Bluetooth Low Energy)。Edge101WE 主板支持双模蓝牙,即同时支持经典蓝牙和蓝牙低功耗。从整体结构上,蓝⽛可分为控制器器 (Controller) 和主机 (Host) 两⼤部分:控制器包括了 PHY、Baseband、Link Controller、Link Manager、Device Manager、HCI 等模块,⽤于硬件接口管理、链路管理等;主机则包括了 L2CAP、SMP、SDP、ATT、GATT、GAP 以及各种规范,构建了向应用层提供接口的基础,方便便应用层对蓝牙系统的访问。主机可以与控制器运行在同⼀个宿主上,也可以分布在不同的宿主上。Edge101WE 主板可以支持上述两种方式。
11.1 Bluetooth Classic 经典蓝牙(BluetoothSerial 蓝牙串口)
BluetoothSerial蓝牙串口,可使用经典蓝牙方式在电脑或者手机上识别到一个串口设备,可通过此串口设备对主板的参数进行配置,或用于其他收发数据的场景。
API参考
available() - 获取可以从蓝牙串行端口读取的字节数
语法
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
int BluetoothSerial::available(void);
参数
无
返回
| 返回值 | 说明 | 值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 可读取的字节数 |
begin() - 启动蓝牙串行设备
注册蓝牙设备的本地名称,然后启动蓝牙串行设备。
语法
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
bool BluetoothSerial::begin(String localName, bool isMaster);
参数
| 传入值 | 说明 | 值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| localName | 本地名称。如果省略,则设置String() | |
| isMaster | 是Master吗?默认为false。 |
返回
| 返回值 | 说明 | 值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| bool | true:启动成功。 false:启动不成功 |
read() - 读取从蓝牙串行端口接收的数据
语法
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
int BluetoothSerial::read(void);
参数
无
返回
| 返回值 | 说明 | 值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 接收到的数据的第一个字节。如果没有收到数据,则为0。 |
write() - 读取从蓝牙串行端口接收的数据
语法
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
size_t BluetoothSerial::write(uint8_t c);
size_t BluetoothSerial::write(const uint8_t *buffer, size_t size);
参数
| 传入值 | 说明 | 值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| c | 要发送的值(1个字节) | |
| buffer | 数据以字节字符串的形式发送 | |
| size | 数据大小 |
返回
| 返回值 | 说明 | 值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| size_t | 发送的字节数 |
例程:SerialToSerialBT
主板蓝牙工作在Bluetooth Classic模式,生成一个蓝牙串口
(参考Arduino IDE例程 Examples -> Examples for Edge101WE ->BluetoothSerial\examples\SerialToSerialBT)
//This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
//By Evandro Copercini - 2018
//
//This example creates a bridge between Serial and Classical Bluetooth (SPP)
//and also demonstrate that SerialBT have the same functionalities of a normal Serial
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
#if !defined(CONFIG_BT_ENABLED) || !defined(CONFIG_BLUEDROID_ENABLED)
#error Bluetooth is not enabled! Please run `make menuconfig` to and enable it
#endif
BluetoothSerial SerialBT;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SerialBT.begin("Edge101WE_Device"); //Bluetooth device name
Serial.println("The device started, now you can pair it with bluetooth!");
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) {
SerialBT.write(Serial.read());
}
if (SerialBT.available()) {
Serial.write(SerialBT.read());
}
delay(20);
}
在安卓系统手机上安装 Serial Bluetooth Terminal 软件。手机打开蓝牙,搜索到 Edge101WE_Device 这个蓝牙设备连接上后打开 Serial Bluetooth Terminal 软件选择 Edge101WE_Device 设备。连接后可在界面上发送数据到主板,主板串口将打印出手机发送的数据。同时主板也可以通过串口发送数据到手机。
例程:带配对功能的蓝牙串口
(参考Arduino IDE例程 Examples -> Examples for Edge101WE ->BluetoothSerial/examples/SerialToSerialBT_SSP_pairing)
//This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
//By Richard Li - 2020
//
//This example creates a bridge between Serial and Classical Bluetooth (SPP with authentication)
//and also demonstrate that SerialBT have the same functionalities of a normal Serial
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
#if !defined(CONFIG_BT_ENABLED) || !defined(CONFIG_BLUEDROID_ENABLED)
#error Bluetooth is not enabled! Please run `make menuconfig` to and enable it
#endif
BluetoothSerial SerialBT;
boolean confirmRequestPending = true;
void BTConfirmRequestCallback(uint32_t numVal)
{
confirmRequestPending = true;
Serial.println(numVal);
}
void BTAuthCompleteCallback(boolean success)
{
confirmRequestPending = false;
if (success)
{
Serial.println("Pairing success!!");
}
else
{
Serial.println("Pairing failed, rejected by user!!");
}
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
SerialBT.enableSSP();
SerialBT.onConfirmRequest(BTConfirmRequestCallback);
SerialBT.onAuthComplete(BTAuthCompleteCallback);
SerialBT.begin("ESP32test"); //Bluetooth device name
Serial.println("The device started, now you can pair it with bluetooth!");
}
void loop()
{
if (confirmRequestPending)
{
if (Serial.available())
{
int dat = Serial.read();
if (dat == 'Y' || dat == 'y')
{
SerialBT.confirmReply(true);
}
else
{
SerialBT.confirmReply(false);
}
}
}
else
{
if (Serial.available())
{
SerialBT.write(Serial.read());
}
if (SerialBT.available())
{
Serial.write(SerialBT.read());
}
delay(20);
}
}
打开手机蓝牙,在蓝牙设置页面搜索到 “ESP32test” 蓝牙设备,点击配对,此时配对页面将会显示一个随机的配对码(例程中显示的 586767),同时主板USB串口也会打印出一个配对码,如果配对码相同说明手机当前是在和当前的主板进行配对。通过串口发送字符 ‘Y’ 或 ‘y’ 进行确认。显示配对成功。此时可以通过手机端安装的 Serial Bluetooth Terminal 进行通信。
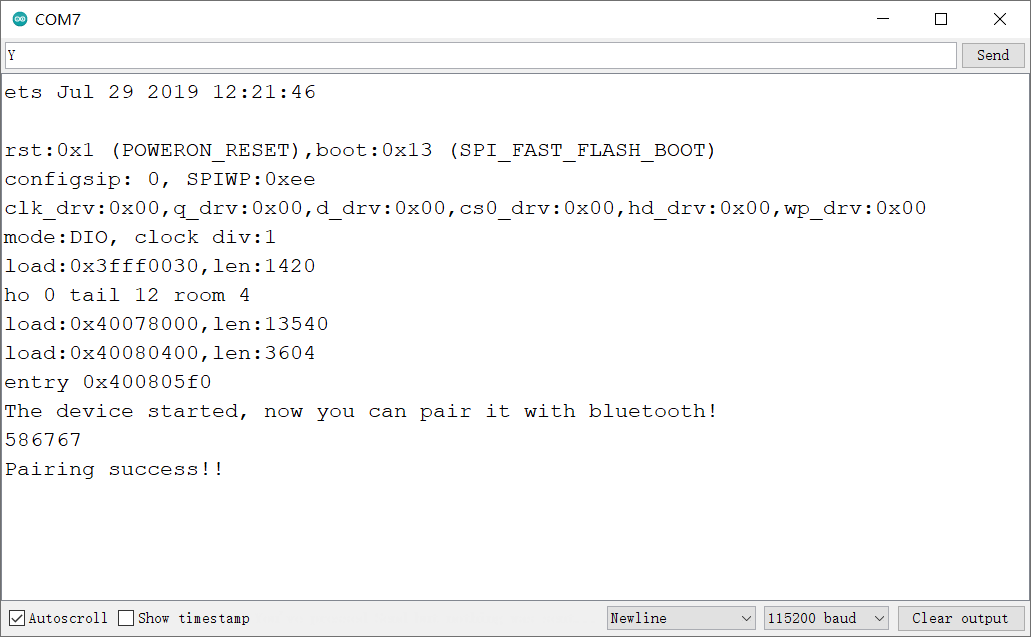
手机发送数据
串口输出
The device started, now you can pair it with bluetooth!
586767
Pairing success!!
This is phone speaking
11.2 BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy低功耗蓝牙)
低功耗蓝牙(BLE)是蓝牙的一种节能形式。BLE 的主要应用是少量数据的短距离传输(低带宽)。与始终打开的蓝牙不同,BLE 始终保持睡眠模式,除非启动连接时。这使其功耗非常低。BLE 的功耗比蓝牙低约100倍(取决于使用情况)。
由于其特性,BLE 适用于需要纽扣电池上定期运行的少量数据的应用。例如 BLE 在医疗保健、健身、跟踪、信标、安全和家庭自动化行业中具有很大的用途。
使用低功耗蓝牙,设备有两种:服务器 (Server)和客户端(Client)。Edge101WE 主板既可以充当客户端,也可以充当服务器。服务器通告其存在,以便其他设备可以找到它,并包含客户端可以读取的数据。客户端扫描附近的设备,并在找到要查找的服务器时建立连接并监听传入的数据。这称为点对点通信。
如果想要让主板处于别人随时可以搜索连接的情况要配置为服务端。如果想让主板通过扫描连接周围可连接的蓝牙设备,需要把它设置成客户端,正好和WiFi模式的设定相反。
BLE 通用访问规范 (GAP) 接口 API 的实现和使用流程,GAP 协议层定义了 BLE 设备的发现流程,设备管理和设备接的建立。BLE GAP 协议层采用 API 调用和事件 (Event) 返回的设计模式,通过事件返回来获取 API在协议栈的处理结果。当对端设备主动发起请求时,也是通过事件返回获取对端设备的状态。
BLE 设备定义了四类 GAP 角色:
广播者 (Broadcaster):处于这种角色的设备通过发送广播 (Advertising) 让接收者发现自己。这种角色只能发广播,不能被连接。
观察者 (Observer):处于这种角色的设备通过接收广播事件并发送扫描 (Scan) 请求。这种角色只能发送扫描请求,不能被连接。
外围设备 (Peripheral):当广播者接受了观察者发来的连接请求后就会进入这种角色。当设备进入了这种角色之后,将会作为从设备 (Slave) 在链路路中进⾏行行通信。
中央设备 (Central):当观察者主动进⾏行行初始化,并建⽴立⼀一个物理理链路路时就会进⼊入这种角色。这种角色在链路路中同样被称为主设备 (Master)。
ATT 属性协议
BLE 里面的数据以属性 (Attribute) 方式存在,每条属性由四个元素组成:
属性句柄 (Attribute Handle):正如我们可以使用内存地址查找内存中的内容一样,ATT 属性的句柄也可以协助我们找到相应的属性,例如第一个属性的句柄是0x0001,第二个属性的句柄是 0x0002,以此类推,最大可以到 0xFFFF。
属性类型 (Attribute UUID):每个数据有自己需要代表的意思,例如表示温度、发射功率、电池等各种各样的信息。蓝牙组织 (Bluetooth SIG) 对常用的一些数据类型进行了归类,赋予不同的数据类型不同的标识码 (UUID)。例例如 0x2A09 表示电池信息,0x2A6E 表示温度信息。UUID 可以是 16 比特的 (16-bit UUID),也可以是 128 比特的 (128-bit UUID)。
属性值 (Attribute Value):属性值是每个属性真正要承载的信息,其他 3 个元素都是为了让对方能够更好地获取属性值。有些属性的长度是固定的,例例如电池属性(Battery Level) 的长度只有 1 个字节,因为需要表示的数据仅有 0~100%,而 1 个字节足以表示 1~100 的范围;而有些属性的长度是可变的,例如基于 BLE 实现的透传模块。
属性许可 (Attribute Permissions):每个属性对各自的属性值有相应的访问限制,比如有些属性是可读的、有些是可写的、有些是可读又可写的等。拥有数据的一方可以通过属性许可,控制本地数据的可读写属性。
| 属性句柄 (Attribute Handle) | 属性类型 (Attribute UUID) | 属性值 (Attribute Value) | 属性许可 (Attribute Permissions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0001 | 0x2A09 表示电池信息 | 100% | 可读 |
| 0x0002 | 0x2A6E 表示温度信息 | 28摄氏度 | 可读 |
| ……… | |||
| 0xFFFE | |||
| 0xFFFF |
我们把存有数据(即属性)的设备叫做服务器 (Server),而将获取别人设备数据的设备叫做客户端 (Client)。下面是服务器和客户端间的常用操作:
客户端给服务端发数据,通过对服务器的数据进行写操作 (Write),来完成数据发送工作。写操作分两种,一种是写入请求 (Write Request),一种是写入命令 (WriteCommand),两者的主要区别是前者需要对方回复响应 (Write Response),而后者不需要对方回复响应。
服务端给客户端发数据,主要通过服务端指示 (Indication) 或者通知 (Notification) 的形式,实现将服务端更新的数据发给客户端。与写操作类似,指示和通知的主要区别是前者需要对方设备在收到数据指示后,进行回复 (Confirmation)。
客户端也可以主动通过读操作读取服务端的数据。
服务器和客户端之间的交互操作都是通过上述的消息 ATT PDU 实现的。每个设备可以指定自己设备支持的最大 ATT 消息长度,我们称之为 MTU。Edge101WE 主板里面规定 MTU 可以设置的范围是 23~517 字节,对属性值的总长度没有做限制。如果用户需要发送的数据包长度大于 (MTU-3),则需要调用准入写入请求 (Prepare WriteRequest) 来完成数据的写操作。同理理,在读取一个数据时候,如果数据的长度超过 (MTU-1),则需要通过大对象读取请求 (Read Blob Request) 来继续读取剩余的值。
GATT 规范
GATT是“通用属性配置文件”(Generic Attribute Profile)的缩写。ATT 属性协议规定了在 BLE 中的最小数据存储单位,而 GATT 规范则定义了一个层次化的数据结构,及其如何用特性值和描述符表示一个数据,如何把相似的数据聚合成服务 (Service),以及如何发现对端设备拥有哪些服务和数据。这意味着 GATT 定义了两个 BLE 设备发送和接收标准消息的方式。 GATT 规范引进了特性值的概念。这是由于在某些时候,一个数据可能并不只是单纯的数值,还会带有一些额外的信息:
比如这个数据的单位是什么?是重量单位千克 kg、温度单位摄⽒氏度 ℃,还是其他单位;
比如希望具体告知对方这个数值的名称,例如同为温度属性 UUID 下,希望告知对方该数据表示“主卧温度”,另一个数据表示“客厅温度”;
比如在表示 230000、460000 等大数据时,可以增加指数信息,告知对方该数据的指数是 10^4,这样仅需在空中传递 23、46 即可。
上述内容仅为清楚描述一个数据众多需求中的几个例子,实际应用中还可能出现其他以各种方式表达的数据需求。为了包含这些信息,每个属性中均需要安排一⼤大段数据空间,存储这些额外信息。然而,一个数据很有可能用不到绝大部分的额外信息,因此这种设计并这不符合 BLE “协议尽可能精简”的要求。在此背景下,GATT 规范引进了描述符的概念,每种描述符可以表达一种意思,用户可使用描述符,描述数据的额外信息。必需说明的是,每个数据和描述符并非一 一对应,即一个复杂的数据可以拥有多个描述符,而一个简单的数据可以没有任何描述符。
数据本身的属性值及其可能携带的描述符,构成了特性 (Characteristic)的概念。数据特性包含以下几个部分:
特性声明 (Characteristic Declaration):主要告诉对方此声明后面跟的内容为特性数值。从当前特性声明开始到下一个特性声明之间的所有句柄 (Handle) 将构成一个完整的特性。此外,特性声明还包括紧跟其后的特性数值的可写可读属性信息。
特性数值 (Characteristic Value):特性的核心部分,一般紧跟在特性声明后⾯面,承载特性的真正内容。
描述符 (Descriptor):描述符可以对特性进行进一步描述,每个特性可以有多个描述符,也可以没有描述符。
BLE 协议中会把一些常用的功能定义成一个个的服务 (Service),例如把电池相关的特性和行为定义成电池服务 (Battery Service);把心率测试相关的特性和行为定义成心跳服务(Heart Rate Service);把体重测试相关的特性和行为定义成体重服务 (Weight ScaleService)。可以看到,每个服务包含若干个特性,每个特性包含若干个描述符。用户可以根据自己的应用需求选择需要的服务,并组成最终的产品应用。 一个完整服务的特性定义参考如下:
| 属性句柄 | 属性类型 |
|---|---|
| 0x0001 | 服务 1 |
| 0x0002 | 特性声明 1 |
| 0x0003 | 特性数值 1 |
| 0x0004 | 描述符 1 |
| 0x0005 | 特性声明 2 |
| 0x0006 | 特性数值 2 |
| 0x0007 | 描述符 2 |
| 0x0008 | 描述符 3 |
| 0x0009 | 服务 2 |
| ……… | ……… |
GATT 已经成为 BLE 通信的规定,每一个设备中存在很多的 “service” (服务),service 中还包含有多个 “Characteristic”(特征值)。 在蓝牙实际数据交换中,就是通过读写这些 “Characteristic”(特征值) 来实现的。
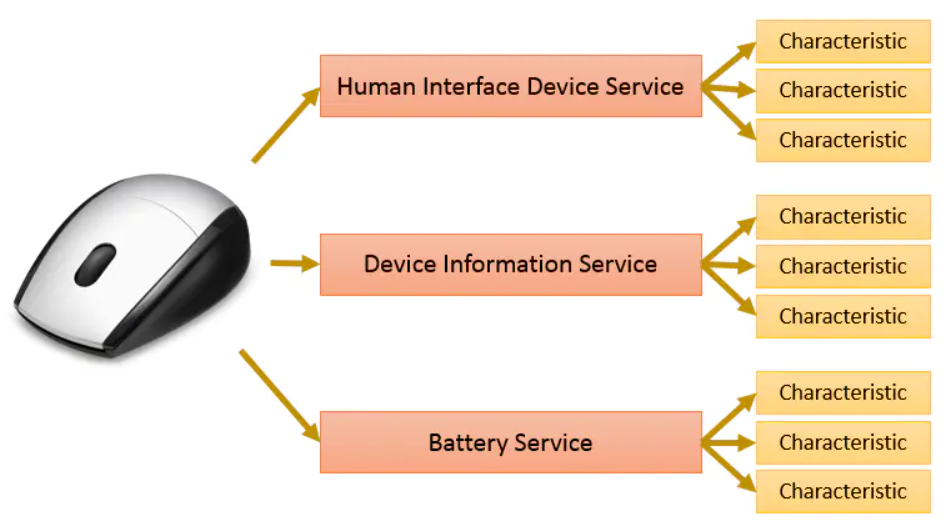
一个鼠标是一个 BLEDevice
一个 BLEDevice 建立了一个BLE服务器 BLEServer
一个 BLE 服务器里有多个服务 BLEService
一个服务里有多个特征值 BLECharacteristic 每个特征值是一种数据.就是通过读写这些 “Characteristic” 实现读写数据
每个 characteristic 的值可以在不加密的状态下读写,但配对的操作是加密的。 还有当 characteristic 的值已改变时,可接收通知(notify)。
UUID
服务和 characteristic 是通过 UUID 来进行识别的。
UUID 是32位的,但那些被蓝牙技术联盟的标准中定义的 UUID 是以四个数字来表示的。UUID 既有16位的也有128位的,我们需要了解的是16位的 UUID 是经过蓝牙组织认证的,是需要购买的,当然也有一些通用的16位 UUID。
UUID:由蓝牙设备厂商提供的 UUID,UUID是在硬件编程里已经确定了的,想要操作特定的服务、特征值都需要通过 UUID 来找。
notify通知的概念
如果主机的一个特征值 characteristic 发生改变, 可以使用通知notify来告诉客户端. 这是服务器主动给客户端发的信息, 并非是响应客户端的请求.
这样做有很多好处, 比如 Edge101WE 主板采集到了温度的变化, 可以将数据写入对应的特征值 characteristic, 然后 notify 通知客户端.
我们创建特征值时, 把它规定为通知类型, 当这个特征值发生变化时,可以通知客户端,像这样:
pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX, BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_NOTIFY);
//创建一个(读)特征值, 它是通知下发类型的特征值
其实客户端可以不接受服务器发送的 notify, 方法是修改自己的 Descriptor. BLE 服务器看到你对自己的描述中标识了不想接收 notify, 也就不会再给你发了。
write写入的概念
我们可以把特征值定为写入类型, 这样客户端可以给我们写入, 触发写入回调函数
BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX, BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE);
//创建一个(写)特征, 它是写入类型的特征值
pCharacteristic->setCallbacks(new MyCallbacks());
//为特征添加一个回调
例程:SimpleBLE
程序将建立一个 BLE 设备,当按下主板的用户按钮时,将修改 BLE 设备的名字,可通过手机查看 BLE 设备的名字变化。
(参考Arduino IDE例程 Examples -> Examples for Edge101WE ->SimpleBLE/examples/SimpleBleDevice)
// Copyright 2015-2016 Espressif Systems (Shanghai) PTE LTD
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
// Sketch shows how to use SimpleBLE to advertise the name of the device and change it on the press of a button
// Useful if you want to advertise some sort of message
// Button is attached between GPIO 0 and GND, and the device name changes each time the button is pressed
#include "SimpleBLE.h" //使用库SimpleBLE
#if !defined(CONFIG_BT_ENABLED) || !defined(CONFIG_BLUEDROID_ENABLED)
#error Bluetooth is not enabled! Please run `make menuconfig` to and enable it
#endif
SimpleBLE ble;
void onButton(){
String out = "BLE32 name: ";
out += String(millis() / 1000);
Serial.println(out);
ble.begin(out); // 修改BLE的名字
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.setDebugOutput(true);
pinMode(38, INPUT_PULLUP); //GPIO38 主板的用户按钮,用于改变BLE设备名字
Serial.print("Edge101WE SDK: ");
Serial.println(ESP.getSdkVersion());
ble.begin("Edge101WE SimpleBLE");//在设备上启用蓝牙后,连接到FireBeetle MESH SimpleBLE。按下按钮时,更改设备名称。
Serial.println("Press the button to change the device's name");
}
void loop() {
static uint8_t lastPinState = 1;
uint8_t pinState = digitalRead(38); //读取GPIO38 主板的用户按钮电平状态
if(!pinState && lastPinState){
onButton();
}
lastPinState = pinState;
while(Serial.available()) Serial.write(Serial.read());
}
例程: BLE Server
/*
Based on Neil Kolban example for IDF: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/blob/master/cpp_utils/tests/BLE%20Tests/SampleServer.cpp
Ported to Arduino ESP32 by Evandro Copercini
updates by chegewara
*/
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting BLE work!");
BLEDevice::init("Long name works now");
BLEServer *pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID);
BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE
);
pCharacteristic->setValue("Hello World says Neil");
pService->start();
// BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = pServer->getAdvertising(); // this still is working for backward compatibility
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = BLEDevice::getAdvertising();
pAdvertising->addServiceUUID(SERVICE_UUID);
pAdvertising->setScanResponse(true);
pAdvertising->setMinPreferred(0x06); // functions that help with iPhone connections issue
pAdvertising->setMinPreferred(0x12);
BLEDevice::startAdvertising();
Serial.println("Characteristic defined! Now you can read it in your phone!");
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
delay(2000);
}
在手机安装 nRF Connect 应用,打开手机蓝牙。在 nRF Connect 应用上连接 “Long name works now” 这个蓝牙设备,即可读取回特征值 “Hello World says Neil”。
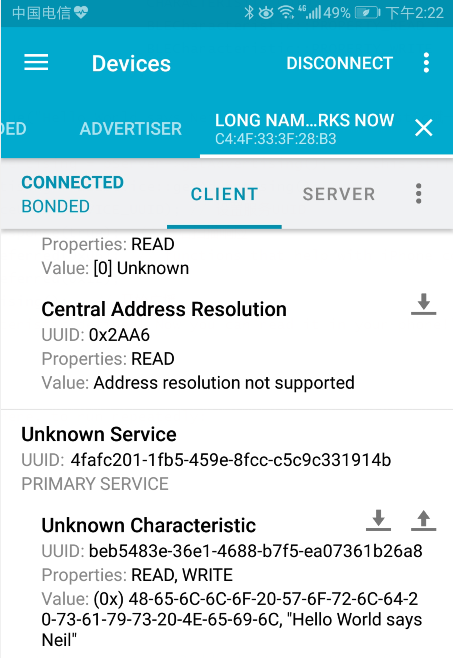
例程:BLE Server_multicconnect
创建一个 BL E服务器,一旦收到连接,它将定期发送通知。
使用步骤
创建一个 BLE Server
创建一个 BLE Service
在 BLE Service 的基础上创建一个 Characteristic
在 Characteristic 的基础上创建一个 Descriptor
启动 Service
开始广播
/*
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oCMOYS71NIU
Based on Neil Kolban example for IDF: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/blob/master/cpp_utils/tests/BLE%20Tests/SampleNotify.cpp
Ported to Arduino ESP32 by Evandro Copercini
updated by chegewara
创建一个BLE服务器,一旦收到连接,它将定期发送通知。
Create a BLE server that, once we receive a connection, will send periodic notifications.
The service advertises itself as: 4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b
And has a characteristic of: beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8
The design of creating the BLE server is:
1. Create a BLE Server
2. Create a BLE Service
3. Create a BLE Characteri stic on the Service
4. Create a BLE Descriptor on the characteristic
5. Start the service.
6. Start advertising.
一个与服务器相关联的连接处理程序将启动一个后台任务,每隔几秒钟发送一次通知。
A connect hander associated with the server starts a background task that performs notification
every couple of seconds.
*/
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLE2902.h>
BLEServer* pServer = NULL;
BLECharacteristic* pCharacteristic = NULL;
bool deviceConnected = false;
bool oldDeviceConnected = false;
uint32_t value = 0;
// 从下列网址生成UUIDs
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
class MyServerCallbacks: public BLEServerCallbacks {
void onConnect(BLEServer* pServer) {
deviceConnected = true; // 如果有设备连接
BLEDevice::startAdvertising(); // 开始广播
};
// 如果无设备
void onDisconnect(BLEServer* pServer) {
deviceConnected = false;
}
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Create the BLE Device
BLEDevice::init("Edge101WE BLE"); // BLE设备初始化
// Create the BLE Server
pServer = BLEDevice::createServer(); // 创建Server
pServer->setCallbacks(new MyServerCallbacks()); // 设置匿名回调函数(实例化MyServerCallbacks)
// Create the BLE Service
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID); // 创建BLE Service
// 创建BLE 特征(Characterristic_UUID,长度)
// Create a BLE Characteristic
pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_NOTIFY |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_INDICATE
);
// https://www.bluetooth.com/specifications/gatt/viewer?attributeXmlFile=org.bluetooth.descriptor.gatt.client_characteristic_configuration.xml
// Create a BLE Descriptor
pCharacteristic->addDescriptor(new BLE2902()); // 创建BLE 描述
// Start the service
pService->start(); // 服务启动
// Start advertising
// 定义了一个BLEAdvertising类指针pAdvertising,它指向BLEDevice::getAdvertising()
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = BLEDevice::getAdvertising();
pAdvertising->addServiceUUID(SERVICE_UUID);
pAdvertising->setScanResponse(false);
// 设置值为0x00以不广播该参数
pAdvertising->setMinPreferred(0x0); // set value to 0x00 to not advertise this parameter
BLEDevice::startAdvertising(); // 开始广播
Serial.println("Waiting a client connection to notify...");
}
void loop() {
// notify changed value
// 如果设备已连接
if (deviceConnected) {
pCharacteristic->setValue((uint8_t*)&value, 4); // 设置值为value
pCharacteristic->notify(); // 发送通知 notify
value++; // value自加
// 可修改发送通知的延迟,便于手机端观察值的变化
delay(1000); // bluetooth stack will go into congestion, if too many packets are sent, in 6 hours test i was able to go as low as 3ms
}
// disconnecting
if (!deviceConnected && oldDeviceConnected) {
delay(500); // give the bluetooth stack the chance to get things ready
pServer->startAdvertising(); //重新广播 restart advertising
Serial.println("start advertising");
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
// connecting
if (deviceConnected && !oldDeviceConnected) {
// do stuff here on connecting
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
}
打开手机蓝牙,在 nRF Connect 应用上连接 “Edge101WE” 这个蓝牙设备,在 Service 列表,点击三个箭头的图标可读取回特征值,可查看 Value 每秒钟数值加一次。
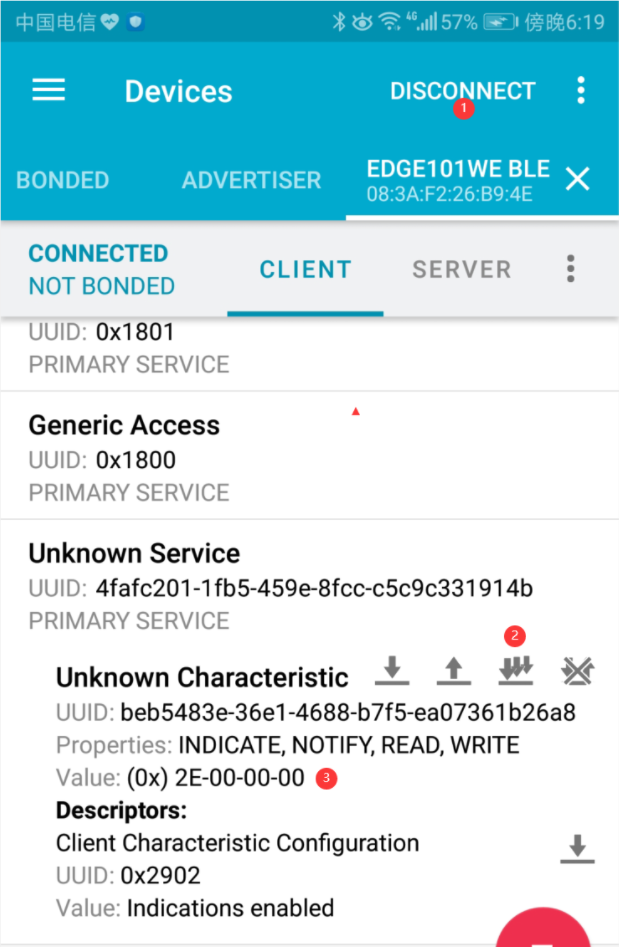
例程:BLE_uart
BLE 的异步通信及安卓 app 测试
/*
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oCMOYS71NIU
Based on Neil Kolban example for IDF: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/blob/master/cpp_utils/tests/BLE%20Tests/SampleNotify.cpp
Ported to Arduino ESP32 by Evandro Copercini
创建一个BLE服务器,一旦我们收到连接,将会周期性发送通知
Create a BLE server that, once we receive a connection, will send periodic notifications.
The service advertises itself as: 6E400001-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E
Has a characteristic of: 6E400002-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E - used for receiving data with "WRITE"
Has a characteristic of: 6E400003-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E - used to send data with "NOTIFY"
The design of creating the BLE server is:
1. Create a BLE Server
2. Create a BLE Service
3. Create a BLE Characteristic on the Service
4. Create a BLE Descriptor on the characteristic
5. Start the service.
6. Start advertising.
在本例中,rxvalue是接收到的数据(仅在该函数内可访问)。txValue是要发送的数据,在这个例子中每秒递增一个字节。
In this example rxValue is the data received (only accessible inside that function).
And txValue is the data to be sent, in this example just a byte incremented every second.
*/
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLE2902.h>
BLEServer *pServer = NULL; // BLEServer指针 pServer
BLECharacteristic * pTxCharacteristic; // BLECharacteristic指针 pTxCharacteristic
bool deviceConnected = false; // 本次连接状态
bool oldDeviceConnected = false; // 上次连接状态
uint8_t txValue = 0;
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "6E400001-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E" // UART service UUID
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX "6E400002-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX "6E400003-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E"
// 创建MyServerCallbacks类,其继承自BLEServerCallbacks
class MyServerCallbacks: public BLEServerCallbacks {
void onConnect(BLEServer* pServer) {
deviceConnected = true;
};
void onDisconnect(BLEServer* pServer) {
deviceConnected = false;
}
};
// 创建MyCallbacks类,其继承自BLECharacteristicCallbacks
class MyCallbacks: public BLECharacteristicCallbacks {
void onWrite(BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic) {
std::string rxValue = pCharacteristic->getValue(); // 接收信息
// 向串口输出收到的值
if (rxValue.length() > 0) {
Serial.println("*********");
Serial.print("Received Value: ");
for (int i = 0; i < rxValue.length(); i++)
Serial.print(rxValue[i]);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("*********");
}
}
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Create the BLE Device
BLEDevice::init("UART Service");
// Create the BLE Server
pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
pServer->setCallbacks(new MyServerCallbacks()); // 设置回调函数
// Create the BLE Service
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID);
// Create a BLE Characteristic
pTxCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_TX,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_NOTIFY
);
pTxCharacteristic->addDescriptor(new BLE2902());
BLECharacteristic * pRxCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID_RX,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE
);
pRxCharacteristic->setCallbacks(new MyCallbacks()); // 设置回调函数
// Start the service
pService->start(); // 开始服务
// Start advertising
pServer->getAdvertising()->start(); // 开始广播
Serial.println("Waiting a client connection to notify...");
}
void loop() {
if (deviceConnected) {
pTxCharacteristic->setValue(&txValue, 1); // 设置要发送的值为1
pTxCharacteristic->notify(); // 广播
txValue++; // 值自加1
// 如果有太多包要发送,蓝牙会堵塞,所以这里增加一个延迟,可增加延迟方便观察
delay(1000); // bluetooth stack will go into congestion, if too many packets are sent
}
// 如果断开连接 disconnecting
if (!deviceConnected && oldDeviceConnected) {
// 留时间给蓝牙缓冲
delay(500); // give the bluetooth stack the chance to get things ready
pServer->startAdvertising(); // 重新广播restart advertising
Serial.println("start advertising");
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
// 正在连接 connecting
if (deviceConnected && !oldDeviceConnected) {
// do stuff here on connecting
oldDeviceConnected = deviceConnected;
}
}
打开手机蓝牙,在 nRF Connect 应用上连接 ”UART Service” 这个蓝牙设备,在Service列表的 TX Characteristic,点击三个箭头的图标可读取回特征值,可查看Value 值变化。
在 RX Characteristic 点击向上的箭头符号,将数据 “hello” 发送到 Edge101WE 主板。
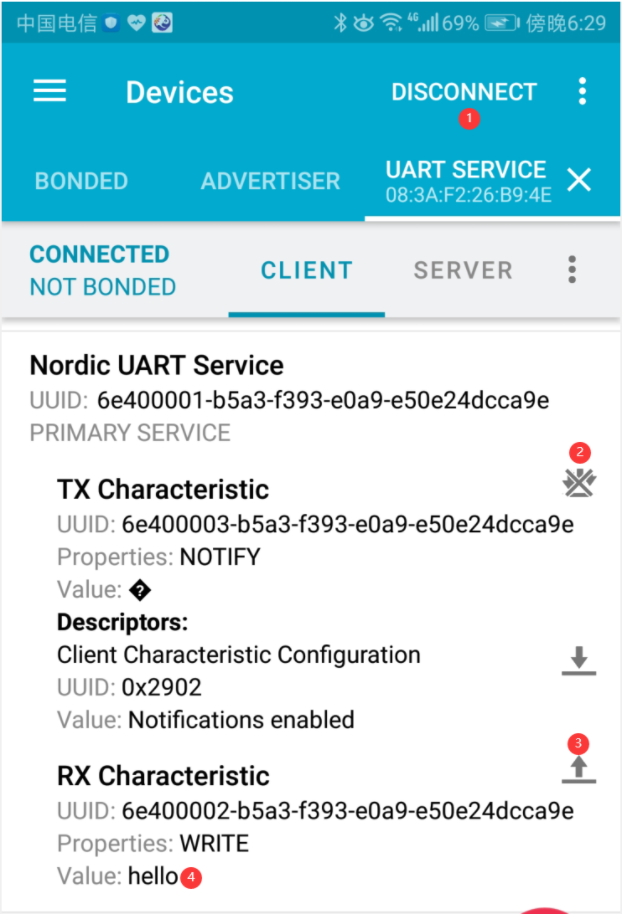
在Arduino IDE的串口打印出接收到的 hello字符串数据。
Waiting a client connection to notify...
*********
Received Value: hello
*********
例程:BLE_write
/*
Based on Neil Kolban example for IDF: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/blob/master/cpp_utils/tests/BLE%20Tests/SampleWrite.cpp
Ported to Arduino ESP32 by Evandro Copercini
*/
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
class MyCallbacks: public BLECharacteristicCallbacks {
void onWrite(BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic) { // 写方法
std::string value = pCharacteristic->getValue(); // 接收值
if (value.length() > 0) {
Serial.println("*********");
Serial.print("New value: ");
for (int i = 0; i < value.length(); i++) // 遍历输出字符串
Serial.print(value[i]);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("*********");
}
}
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("1- Download and install an BLE scanner app in your phone");
Serial.println("2- Scan for BLE devices in the app");
Serial.println("3- Connect to Edge101WE");
Serial.println("4- Go to CUSTOM CHARACTERISTIC in CUSTOM SERVICE and write something");
Serial.println("5- See the magic =)");
BLEDevice::init("Edge101WE"); //设备初始化,名称Edge101WE
BLEServer *pServer = BLEDevice::createServer(); // BLEServer指针,创建Server
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID); // BLEService指针,创建Service
// BLECharacteristic指针,创建Characteristic
BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE
);
pCharacteristic->setCallbacks(new MyCallbacks()); // 设置回调函数
pCharacteristic->setValue("Hello World"); // 设置值 "Hello World"
pService->start(); // 开启服务
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = pServer->getAdvertising(); // 初始化广播
pAdvertising->start(); // 开始广播
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
delay(2000);
}
打开手机蓝牙,在 nRF Connect 应用上连接 “Edge101WE“ 这个蓝牙设备,在 Service 列表的 TX Characteristic,点击向下箭头图标可读取回特征值,当前 Value值为 “Hello World”。
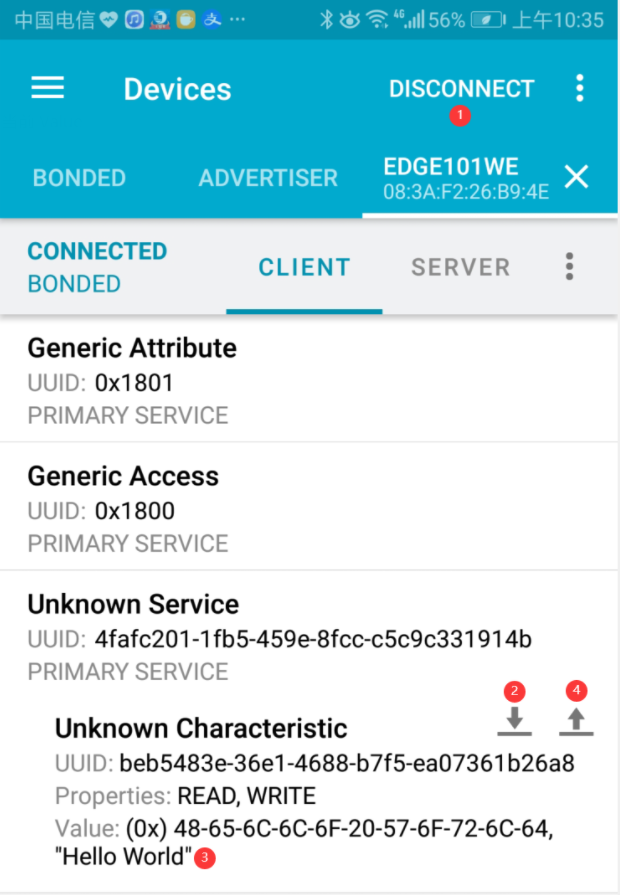
在 Characteristic 点击向上箭头,将数据发送给 Edge101WE 主板。数据类型选择 TEXT,输入 “hello edge101we”,点击 SEND 发送数据。
可以看到串口有打印出接收到的数据。
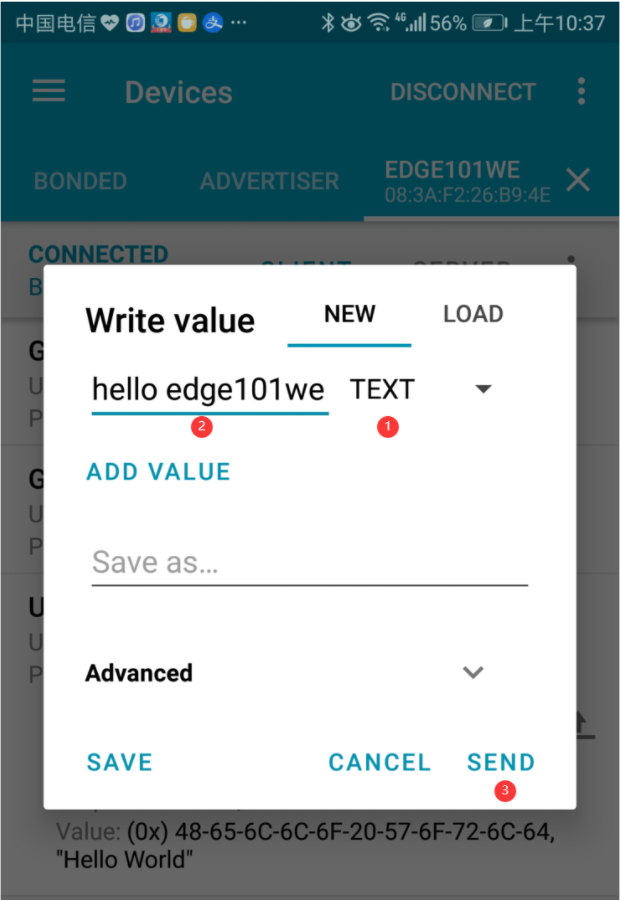
串口打印数据
1- Download and install an BLE scanner app in your phone
2- Scan for BLE devices in the app
3- Connect to Edge101WE
4- Go to CUSTOM CHARACTERISTIC in CUSTOM SERVICE and write something
5- See the magic =)
*********
New value: hello edge101we
*********
此时再次读取 Vaule,发现已经被修改为 “hello edge101we”
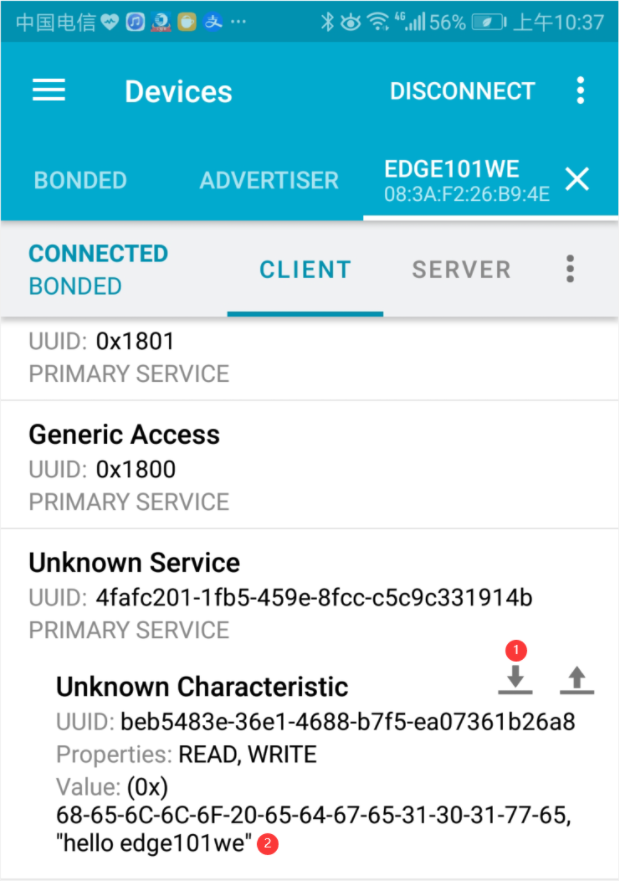
例程:BLE client
配合之前的BLE Server例程演示。使用一块主板烧录BLE Server的例程,另一块主板烧录下方的BLE client的例程
/**
* A BLE client example that is rich in capabilities.
* There is a lot new capabilities implemented.
* author unknown
* updated by chegewara
*/
#include "BLEDevice.h"
//#include "BLEScan.h"
// The remote service we wish to connect to.
static BLEUUID serviceUUID("4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b");
// The characteristic of the remote service we are interested in.
static BLEUUID charUUID("beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8");
static boolean doConnect = false;
static boolean connected = false;
static boolean doScan = false;
static BLERemoteCharacteristic* pRemoteCharacteristic;
static BLEAdvertisedDevice* myDevice;
static void notifyCallback(
BLERemoteCharacteristic* pBLERemoteCharacteristic,
uint8_t* pData,
size_t length,
bool isNotify) {
Serial.print("Notify callback for characteristic ");
Serial.print(pBLERemoteCharacteristic->getUUID().toString().c_str());
Serial.print(" of data length ");
Serial.println(length);
Serial.print("data: ");
Serial.println((char*)pData);
}
class MyClientCallback : public BLEClientCallbacks {
void onConnect(BLEClient* pclient) {
}
void onDisconnect(BLEClient* pclient) {
connected = false;
Serial.println("onDisconnect");
}
};
bool connectToServer() {
Serial.print("Forming a connection to ");
Serial.println(myDevice->getAddress().toString().c_str());
BLEClient* pClient = BLEDevice::createClient();
Serial.println(" - Created client");
pClient->setClientCallbacks(new MyClientCallback());
// Connect to the remove BLE Server.
pClient->connect(myDevice); // if you pass BLEAdvertisedDevice instead of address, it will be recognized type of peer device address (public or private)
Serial.println(" - Connected to server");
// Obtain a reference to the service we are after in the remote BLE server.
BLERemoteService* pRemoteService = pClient->getService(serviceUUID);
if (pRemoteService == nullptr) {
Serial.print("Failed to find our service UUID: ");
Serial.println(serviceUUID.toString().c_str());
pClient->disconnect();
return false;
}
Serial.println(" - Found our service");
// Obtain a reference to the characteristic in the service of the remote BLE server.
pRemoteCharacteristic = pRemoteService->getCharacteristic(charUUID);
if (pRemoteCharacteristic == nullptr) {
Serial.print("Failed to find our characteristic UUID: ");
Serial.println(charUUID.toString().c_str());
pClient->disconnect();
return false;
}
Serial.println(" - Found our characteristic");
// Read the value of the characteristic.
if(pRemoteCharacteristic->canRead()) {
std::string value = pRemoteCharacteristic->readValue();
Serial.print("The characteristic value was: ");
Serial.println(value.c_str());
}
if(pRemoteCharacteristic->canNotify())
pRemoteCharacteristic->registerForNotify(notifyCallback);
connected = true;
return true;
}
/**
* Scan for BLE servers and find the first one that advertises the service we are looking for.
*/
class MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks: public BLEAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks {
/**
* Called for each advertising BLE server.
*/
void onResult(BLEAdvertisedDevice advertisedDevice) {
Serial.print("BLE Advertised Device found: ");
Serial.println(advertisedDevice.toString().c_str());
// We have found a device, let us now see if it contains the service we are looking for.
if (advertisedDevice.haveServiceUUID() && advertisedDevice.isAdvertisingService(serviceUUID)) {
BLEDevice::getScan()->stop();
myDevice = new BLEAdvertisedDevice(advertisedDevice);
doConnect = true;
doScan = true;
} // Found our server
} // onResult
}; // MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting Arduino BLE Client application...");
BLEDevice::init("");
// Retrieve a Scanner and set the callback we want to use to be informed when we
// have detected a new device. Specify that we want active scanning and start the
// scan to run for 5 seconds.
BLEScan* pBLEScan = BLEDevice::getScan();
pBLEScan->setAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks(new MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks());
pBLEScan->setInterval(1349);
pBLEScan->setWindow(449);
pBLEScan->setActiveScan(true);
pBLEScan->start(5, false);
} // End of setup.
// This is the Arduino main loop function.
void loop() {
// If the flag "doConnect" is true then we have scanned for and found the desired
// BLE Server with which we wish to connect. Now we connect to it. Once we are
// connected we set the connected flag to be true.
if (doConnect == true) {
if (connectToServer()) {
Serial.println("We are now connected to the BLE Server.");
} else {
Serial.println("We have failed to connect to the server; there is nothin more we will do.");
}
doConnect = false;
}
// If we are connected to a peer BLE Server, update the characteristic each time we are reached
// with the current time since boot.
if (connected) {
String newValue = "Time since boot: " + String(millis()/1000);
Serial.println("Setting new characteristic value to \"" + newValue + "\"");
// Set the characteristic's value to be the array of bytes that is actually a string.
pRemoteCharacteristic->writeValue(newValue.c_str(), newValue.length());
}else if(doScan){
BLEDevice::getScan()->start(0); // this is just example to start scan after disconnect, most likely there is better way to do it in arduino
}
delay(1000); // Delay a second between loops.
} // End of loop
两块主板复位后,打开client这边的串口监视器,可以看到如下输出
Starting Arduino BLE Client application...
BLE Advertised Device found: Name: Long name works now, Address: 08:3a:f2:26:b5:ea, serviceUUID: 4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b, txPower: 3
Forming a connection to 08:3a:f2:26:b5:ea
Created client
Connected to server
Found our service
Found our characteristic
The characteristic value was: Hello World says Neil
We are now connected to the BLE Server.
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 2"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 3"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 4"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 5"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 6"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 7"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 8"
Setting new characteristic value to "Time since boot: 9"
例程:BLE client 控制外设
Edge101WE 主板作为 BLE 客户端 连接蓝牙手环的服务端。当手环靠近主板,主板上GPIO 15 用户LED灯亮,当离开一定距离 LED灯灭。
此方案可用户办公场所节能,例如人进入房间,房间里面的灯自动打开,当离开房间后灯自动熄灭。或用于工厂机器的安全防护,例如只有佩戴授权ID的蓝牙手环才能去操作此台机器,当操作人员离开后机器自动关闭。
/*
* Program to operate ESP32 in client mode and use fitness band as proximity switch
* Program by: Aswinth Raj B
* Dated: 31-10-2018
* Website: www.circuitdigest.com
* Reference: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets
* //NOTE: The My_BLE_Address, serviceUUID and charUUID should be changed based on the BLe server you are using
*/
#include <BLEDevice.h> //Header file for BLE
static BLEUUID serviceUUID("0000fee7-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb"); //Service UUID of fitnessband obtained through nRF connect application
static BLEUUID charUUID("0000fee7-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb"); //Characteristic UUID of fitnessband obtained through nRF connect application
String My_BLE_Address = "c7:f0:69:f0:68:81"; //Hardware Bluetooth MAC of my fitnessband, will vary for every band obtained through nRF connect application
static BLERemoteCharacteristic* pRemoteCharacteristic;
BLEScan* pBLEScan; //Name the scanning device as pBLEScan
BLEScanResults foundDevices;
static BLEAddress *Server_BLE_Address;
String Scaned_BLE_Address;
boolean paired = false; //boolean variable to togge light
bool connectToserver (BLEAddress pAddress){
BLEClient* pClient = BLEDevice::createClient();
Serial.println(" - Created client");
// Connect to the BLE Server.
pClient->connect(pAddress);
Serial.println(" - Connected to fitnessband");
// Obtain a reference to the service we are after in the remote BLE server.
BLERemoteService* pRemoteService = pClient->getService(serviceUUID);
if (pRemoteService != nullptr)
{
Serial.println(" - Found our service");
return true;
}
else
return false;
// Obtain a reference to the characteristic in the service of the remote BLE server.
pRemoteCharacteristic = pRemoteService->getCharacteristic(charUUID);
if (pRemoteCharacteristic != nullptr)
Serial.println(" - Found our characteristic");
return true;
}
class MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks: public BLEAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks
{
void onResult(BLEAdvertisedDevice advertisedDevice) {
Serial.printf("Scan Result: %s \n", advertisedDevice.toString().c_str());
Server_BLE_Address = new BLEAddress(advertisedDevice.getAddress());
Scaned_BLE_Address = Server_BLE_Address->toString().c_str();
}
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); //Start serial monitor
Serial.println("FireBeetle MESH BLE Server program"); //Intro message
BLEDevice::init("");
pBLEScan = BLEDevice::getScan(); //create new scan
pBLEScan->setAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks(new MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks()); //Call the class that is defined above
pBLEScan->setActiveScan(true); //active scan uses more power, but get results faster
pinMode (15,OUTPUT); //Declare the in-built LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
foundDevices = pBLEScan->start(3); //Scan for 3 seconds to find the Fitness band
while (foundDevices.getCount() >= 1)
{
if (Scaned_BLE_Address == My_BLE_Address && paired == false)
{
Serial.println("Found Device :-)... connecting to Server as client");
if (connectToserver(*Server_BLE_Address))
{
paired = true;
Serial.println("********************LED turned ON************************");
digitalWrite (15,LOW);
break;
}
else
{
Serial.println("Pairing failed");
break;
}
}
if (Scaned_BLE_Address == My_BLE_Address && paired == true)
{
Serial.println("Our device went out of range");
paired = false;
Serial.println("********************LED OF************************");
digitalWrite (15,HIGH);
ESP.restart();
break;
}
else
{
Serial.println("We have some other BLe device in range");
break;
}
}
}